
Introduction to Computer
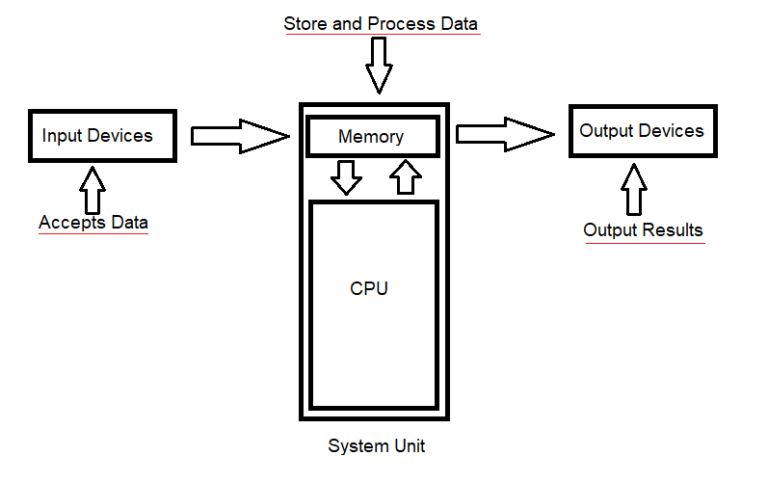
A Computer is an electronic machine that accepts, stores, processes data and provides results or outputs. It is basically a data processing device. We can also define it as “An electronic device that processes data and performs tasks according to a set of instructions given by computer programs and produces desired results. It consists of two types of components hardware and software”
Functions of Computers
Accepts Data: Computers accept data using input devices in different forms like texts, pictures, audio, and video.
Store Data: Computers store data in memory for future use (documents, photos, software).
Process Data: Computers Perform calculations, modify data, and manage information using its processor.
Produce Results: After processing computer provides the desired results using Output devices
Characteristics of Computers
- Speed
High Processing Speed: Computers can process data and perform complex calculations at incredibly high speeds, measured in gigahertz (GHz) for CPUs. This allows for quick execution of tasks. - Accuracy
Precision: Computers perform operations with high precision and accuracy. Errors typically occur due to human input or software bugs, not the computer’s operation itself. - Automation
Automated Operation: Once programmed, computers can perform tasks automatically without human intervention. They follow the instructions in the software to complete tasks consistently. - Storage Capacity
Large Storage: Computers can store vast amounts of data in various storage devices, such as hard drives, SSDs, and cloud storage. This data can be retrieved and processed as needed. - Versatility
Multipurpose: Computers can perform a wide variety of tasks, from word processing and web browsing to complex scientific computations and graphic design. - Diligence
Consistent Performance: Computers do not suffer from fatigue or boredom. They can perform repetitive tasks with the same level of accuracy and efficiency over long periods. - Connectivity
Network Communication: Computers can connect to other computers and networks, enabling data sharing, communication, and access to information over the Internet. - Multitasking
Concurrent Task Handling: Modern computers can run multiple applications simultaneously, allowing users to switch between tasks without performance degradation. - Programmability
Customizable: Computers can be programmed to perform specific tasks by writing software code. This allows for tailored solutions to meet various needs. - Reliability
Dependable Operation: When properly maintained, computers are highly reliable, capable of running without failure for extended periods. - Scalability Expandable: Computer systems can be scaled up or down depending on the requirements. This includes adding more memory, storage, or processing power.
- Interactivity
User Interaction: Computers can interact with users through various input and output devices, providing a responsive and interactive experience. - Security
Data Protection: Modern computers have robust security features to protect data from unauthorized access, including encryption, firewalls, and antivirus software.